Navigating Access Requirements: A Comprehensive Guide to the International Mechanical Code (IMC) Section 306.5
In the realm of building regulations, the International Mechanical Code (IMC) stands as a critical document governing the safe access and maintenance of equipment and appliances located on elevated structures or building roofs. Specifically, Section 306.5 of the IMC outlines stringent criteria for ensuring safe and accessible means of reaching elevated equipment, emphasizing both safety and practicality in design and construction.
Understanding Section 306.5 of the IMC
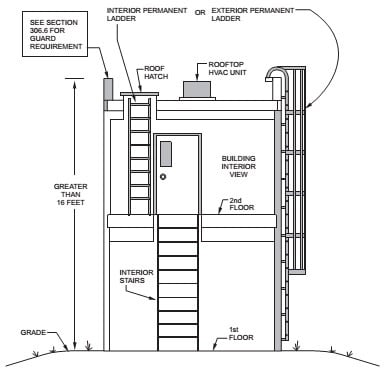
Section 306.5 of the IMC addresses the necessity for providing safe access to equipment or appliances located more than 16 feet (487 cm) above ground level. This regulation mandates that such access should be facilitated without the need for portable ladders and should not require climbing over obstructions exceeding 30 inches (76 cm) in height or navigating roofs with a slope greater than 4 units vertical in 12 units horizontal (33% slope).
Key Criteria and Requirements
- Side Railings: Any access provision must include side railings extending not less than 30 inches (762 mm) above the parapet or roof edge to ensure adequate fall protection.
- Ladder Design: Ladders used for access must adhere to specific design standards:
- Rung spacing should not exceed 14 inches (356 mm) on center.
- The uppermost rung shall be positioned no more than 24 inches (610 mm) below the upper edge of the roof hatch, roof, or parapet.
- Rungs must have a minimum depth of 6 inches (152 mm).
- There should be a minimum clearance of 18 inches (457 mm) between ladder rails.
- Rungs must withstand a load of at least 300 pounds (136.1 kg) and have a diameter not less than 0.75 inches (19 mm).
- Ladder Height: Ladders exceeding 30 feet (9.14 m) in height must include offset sections and landings capable of supporting a load of 100 pounds per square foot (488.2 kg/m2). These landings should be at least 18 inches (457 mm) deep and as wide as the ladder itself, with guardrails on all open sides.
- Clearances and Dimensions: Adequate clearances are essential:
- A minimum distance of 30 inches (762 mm) perpendicular to the ladder rungs should be maintained from the ladder access point to the bottom of the roof hatch.
- A clear width of at least 15 inches (381 mm) on both sides of the ladder, measured from the midpoint of and parallel with the rungs, is required unless cages or wells are installed.
- The bottom landing area of the ladder must be clear and unobstructed, measuring at least 30 inches by 30 inches (762 mm by 762 mm).
- Protection Against Corrosion: To ensure longevity and safety, ladders must be protected against corrosion using approved methods.
- Continuous Access: Access to ladders must be available at all times to facilitate routine maintenance and emergency situations.
- Catwalk Requirements: Catwalks used to provide necessary access must be at least 24 inches (610 mm) wide and equipped with railings as required for service platforms.
Compliance and Safety Assurance
Compliance with Section 306.5 of the IMC is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment and ensuring regulatory adherence in the construction and maintenance of buildings with elevated equipment. By following these detailed criteria, architects, engineers, and building owners can mitigate risks associated with elevated access, promote worker safety, and facilitate efficient maintenance practices.
In conclusion, the IMC Section 306.5 sets a robust standard for the design and construction of access systems to elevated equipment and appliances. By incorporating these specifications into building plans and maintenance protocols, stakeholders can uphold safety, compliance, and operational efficiency in commercial and industrial settings. This adherence not only meets regulatory requirements but also fosters a culture of safety and reliability in building management practices.